Blog
With so much buzz about AI at present, we invite blog post contributions which demystify key topics.
And look out for our news updates!


The intent of the study was to determine the influence of skin type and wavelength on light reflectance for pulse rate detection. PPG sensors detecting changes in blood flow are assessed for effectiveness on dark and light skin tones. Studies have shown that green light lacks precision and accuracy, and may not read at all […]
Read More
The ability to measure physical activity through wrist-worn devices provides an opportunity for cardiovascular medicine. However, the accuracy of commercial devices is largely unknown. The aim of this work is to assess the accuracy of seven commercially available wrist-worn devices in estimating hea… This research paper assesses the accuracy of seven commercially available wrist-worn devices, […]
Read More
This study sheds more light on factors affecting perceived risks and proposes some recommendations on how to practically reduce these concerns. The findings of this study provide implications for research and practice in the area of AI-based CDS. Regulatory agencies, in cooperation with healthcare… This paper examines AI-based tools for healthcare from a consumer’s perspective. […]
Read More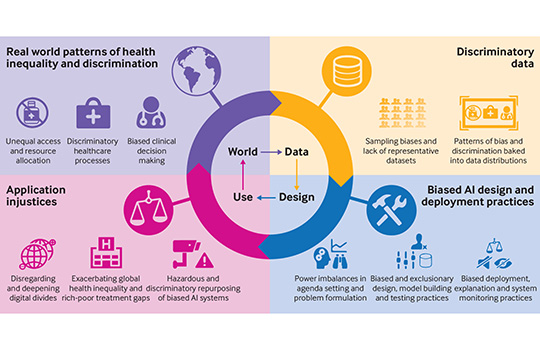
Artificial intelligence can help tackle the covid-19 pandemic, but bias and discrimination in its design and deployment risk exacerbating existing health inequity argue David Leslie and colleagues. Among the most damaging characteristics of the covid-19 pandemic has been its disproportionate effect… A team of medical ethics researchers are arguing that bias and discrimination within AI […]
Read More
The double-edged sword of AI with bias; on the one hand it could treat every patient objectively and reduce bias, and on the other could impact certain patient populations adversely by using non-representative data. This video examines the potential of AI in reducing biases within medical diagnosis, by using AI technologies to understand how diseases […]
Read More
Consumer wearables are devices used for tracking activity, sleep, and other health-related outcomes (e.g. Apple Watch, Fitbit, Samsung, Basis, Mio, PulseOn, Who Consumer wearables are devices used for tracking activity, sleep and other health-related outcomes, intended to help people reach their wellness goals. However these wearables are less accurate for people with darker skin tones, […]
Read More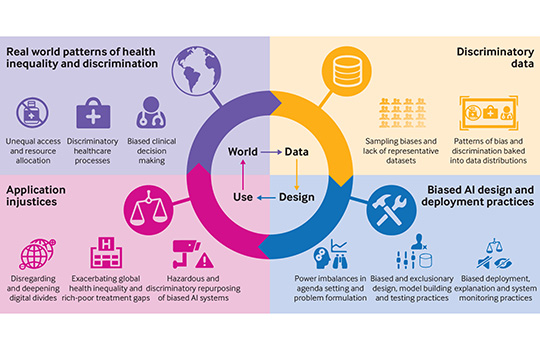
Artificial intelligence can help tackle the covid-19 pandemic, but bias and discrimination in its design and deployment risk exacerbating existing health inequity argue David Leslie and colleagues Among the most damaging characteristics of the covid-19 pandemic has been its disproportionate effect… A team of medical ethics researchers are arguing that bias and discrimination within AI […]
Read More
Medicine and Society from The New England Journal of Medicine — Hidden in Plain Sight — Reconsidering the Use of Race Correction in Clinical Algorithms Physicians still lack consensus on the meaning of race within medical science; there is an ongoing debate as to whether racial and ethnic categories can reflect underlying population genetics, and […]
Read More
This research paper gives arguments for how AI can benefit our education system. It argues that AI can support teachers in giving children the best education whilst not taking away from the humanity of it. AI can be beneficial in aspects such as online tutoring, collaborative learning, and tackling achievement gaps. While it does not […]
Read MoreMeasuring racial discrimination in algorithms There is growing concern that the rise of algorithmic decision-making can lead to discrimination against legally protected groups, but measuring such algorithmic discrimination is often hampered by a fundamental selection challenge. We develop new quasi-experimental tools to overcome this challenge and measure algorithmic discrimination in the setting of pre-trial bail […]
Read More
The impact of artificial intelligence in consumer lending. This US focused report considers four distinct ways of incorporating Artificial Intelligence into credit lending. It highlights the existing racial bias in credit scores, where white / non-hispanic individuals are likely to have a much higher credit score than black / African American individuals. And argues that […]
Read MoreReal toxicity prompts Pre-trained neural language models (LMs) are prone to generating racist, sexist, or otherwise toxic language which hinders their safe deployment. We investigate the extent to which pre-trained LMs can be prompted to generate toxic language, and the effectiveness of controllable text generation algorithms at preventing such toxic degeneration This paper highlights how […]
Read More