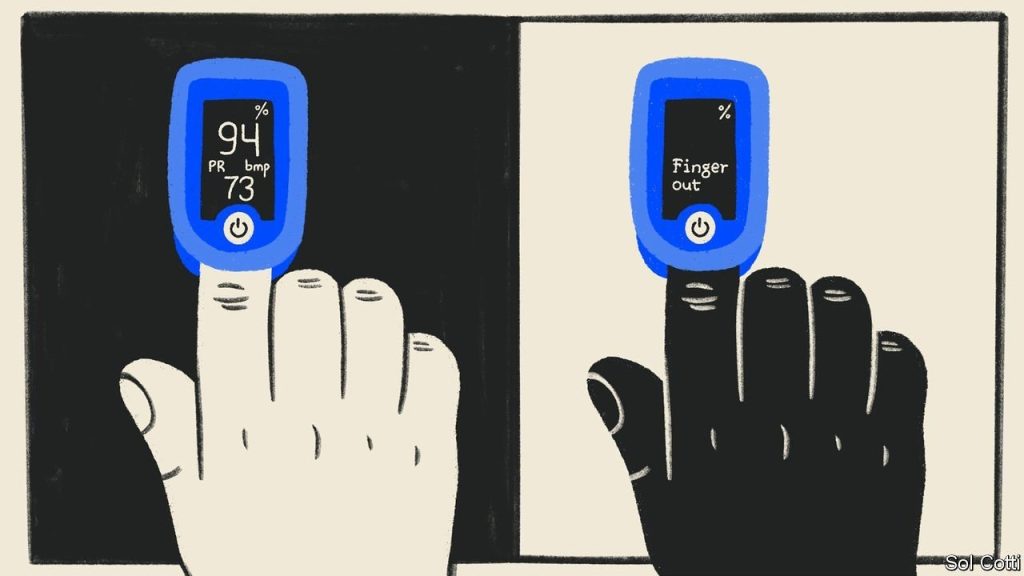
Health Monitoring Devices

Health Monitoring Devices have gained popularity over the past few years, and hold promise in helping people to reach their wellness goals. However, these devices rely on un-representative data-driven algorithms, which leaves ethnic minorities vulnerable to their ineffectiveness.